Bring innovation and higher quality care to your facility or hospital network

























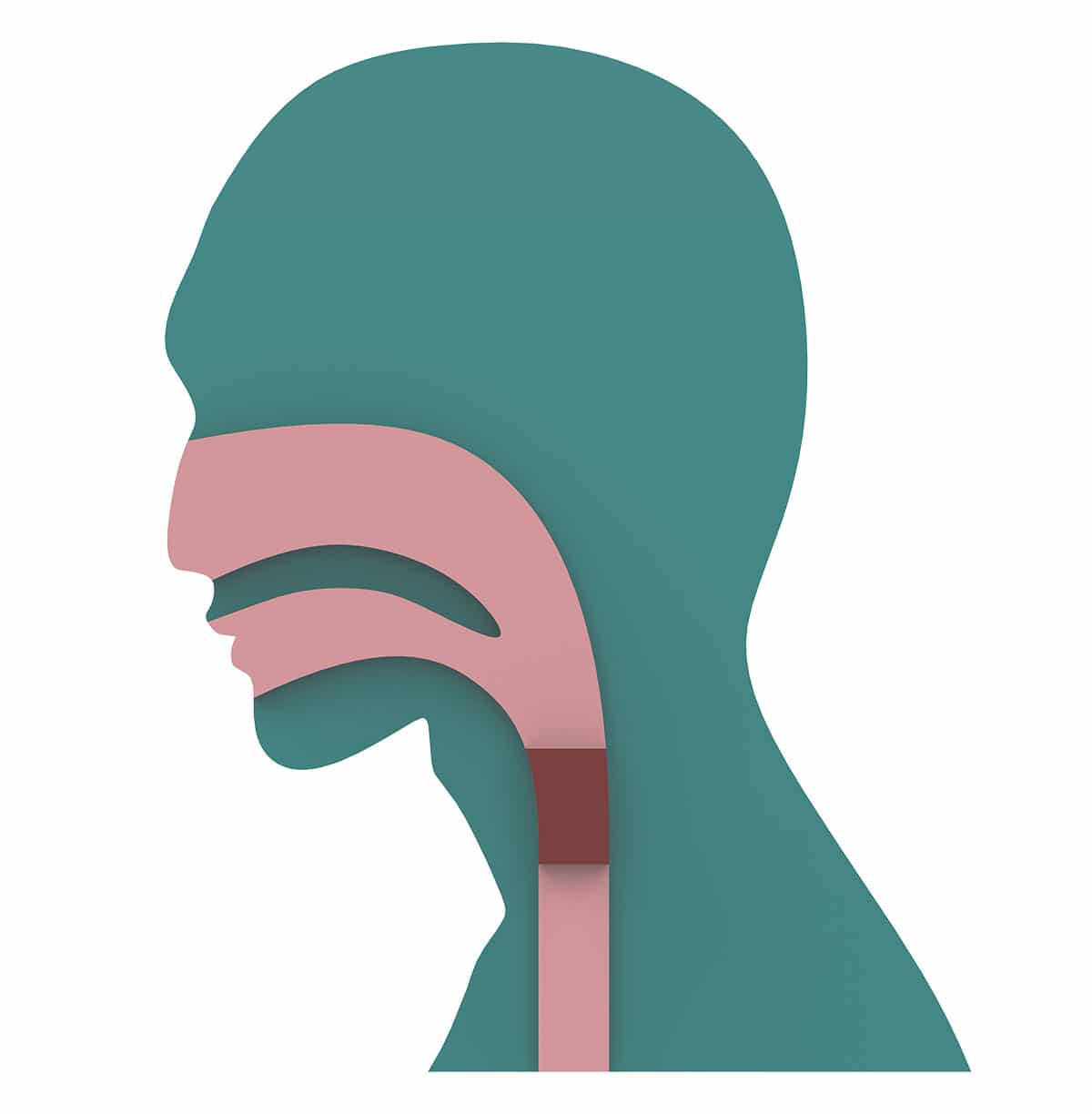
Dysphagia is a common outcome of stroke, head and neck cancer, and neurological conditions like Parkinson’s Disease.
Dysphagia:
- Adds 60% to health care costs1,2
- Is associated with an increased length of stay in hospital1,2
- Is associated with a high rate of hospital readmissions3,4
- Can result in costly consequences, such as aspiration pneumonia and g-tubes5,6
Our Solution
Very simply, we’ve modernized a known therapy technique that has been shown to result in positive outcomes on swallowing function7 such as:
Elimination of feeding tubes8
Improved oral intake8
Clinically-significant improvements in patient-reported outcomes9
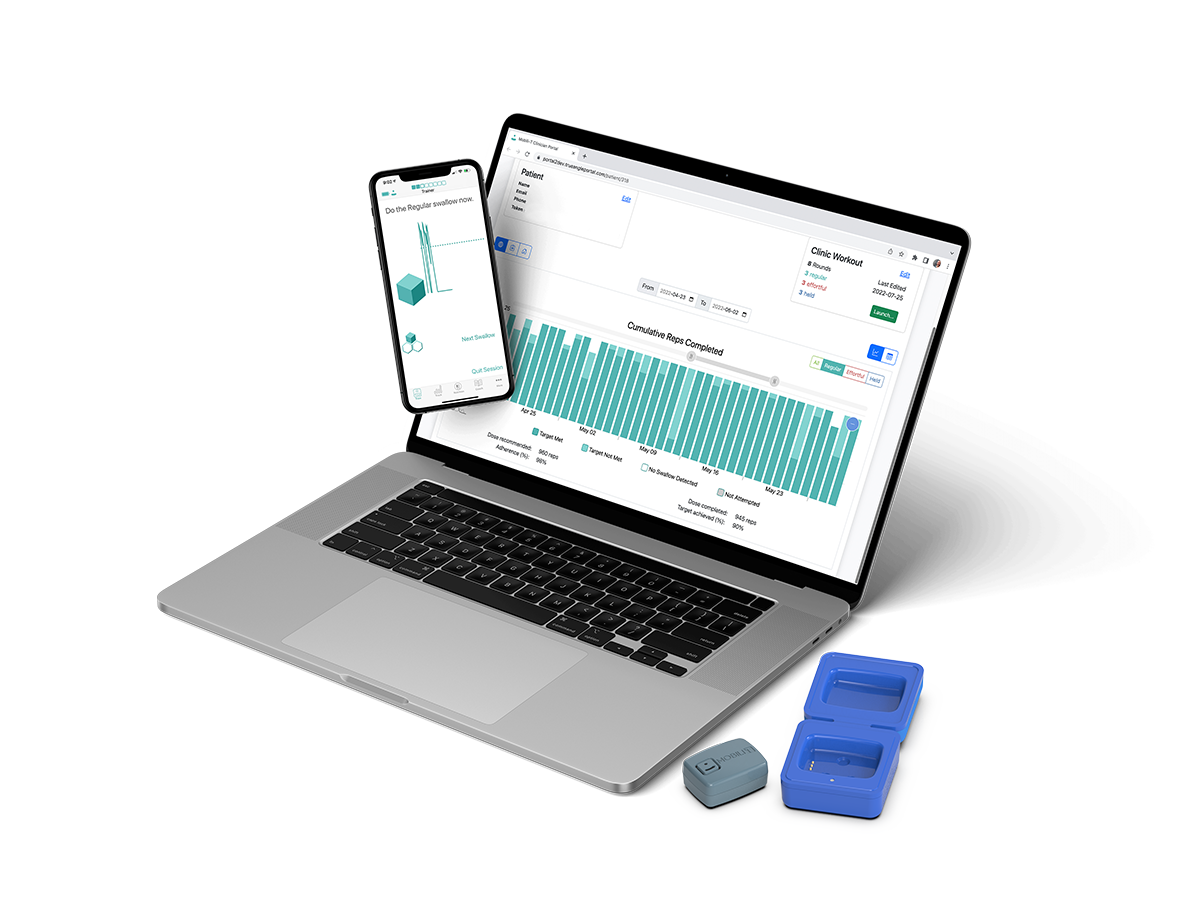
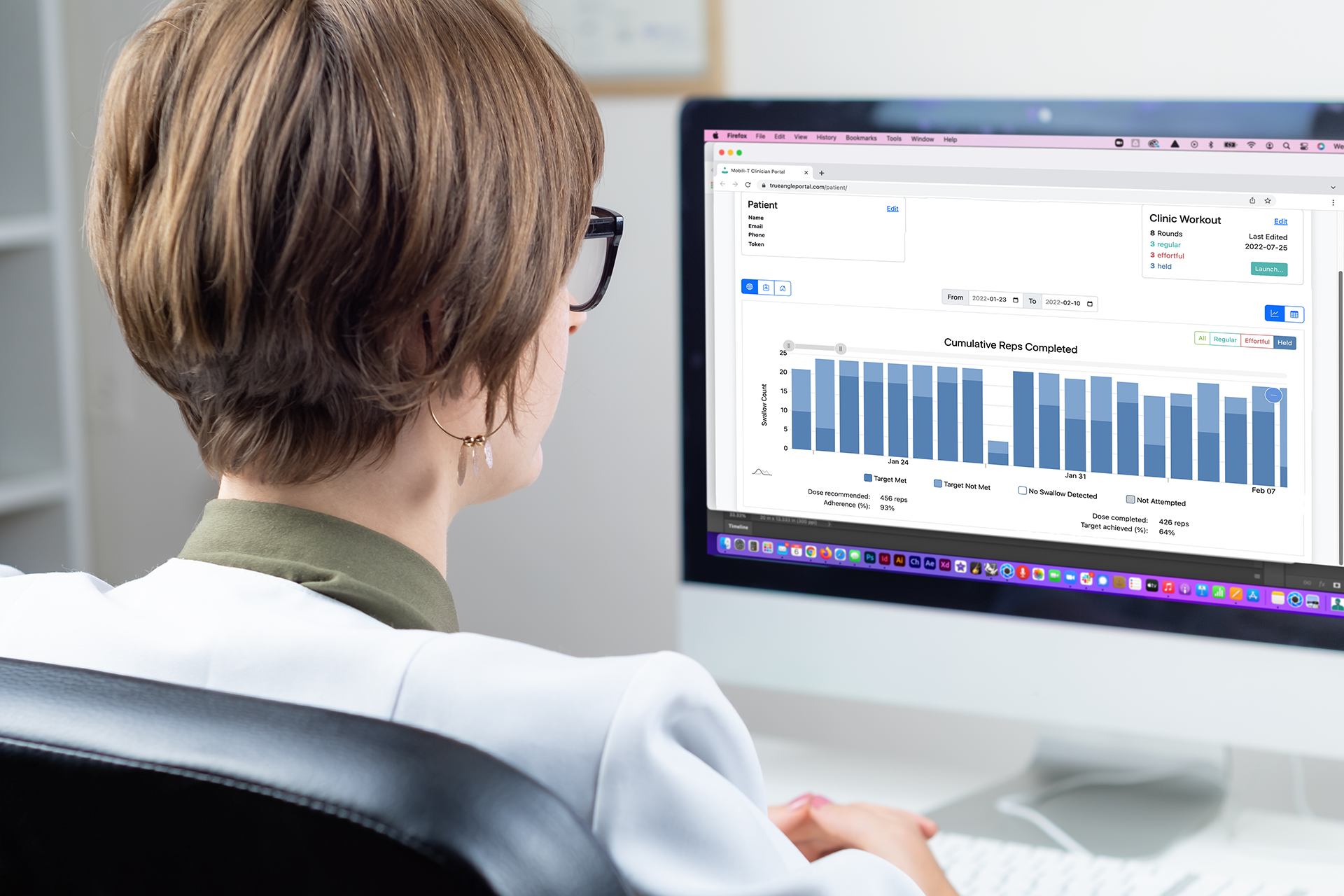
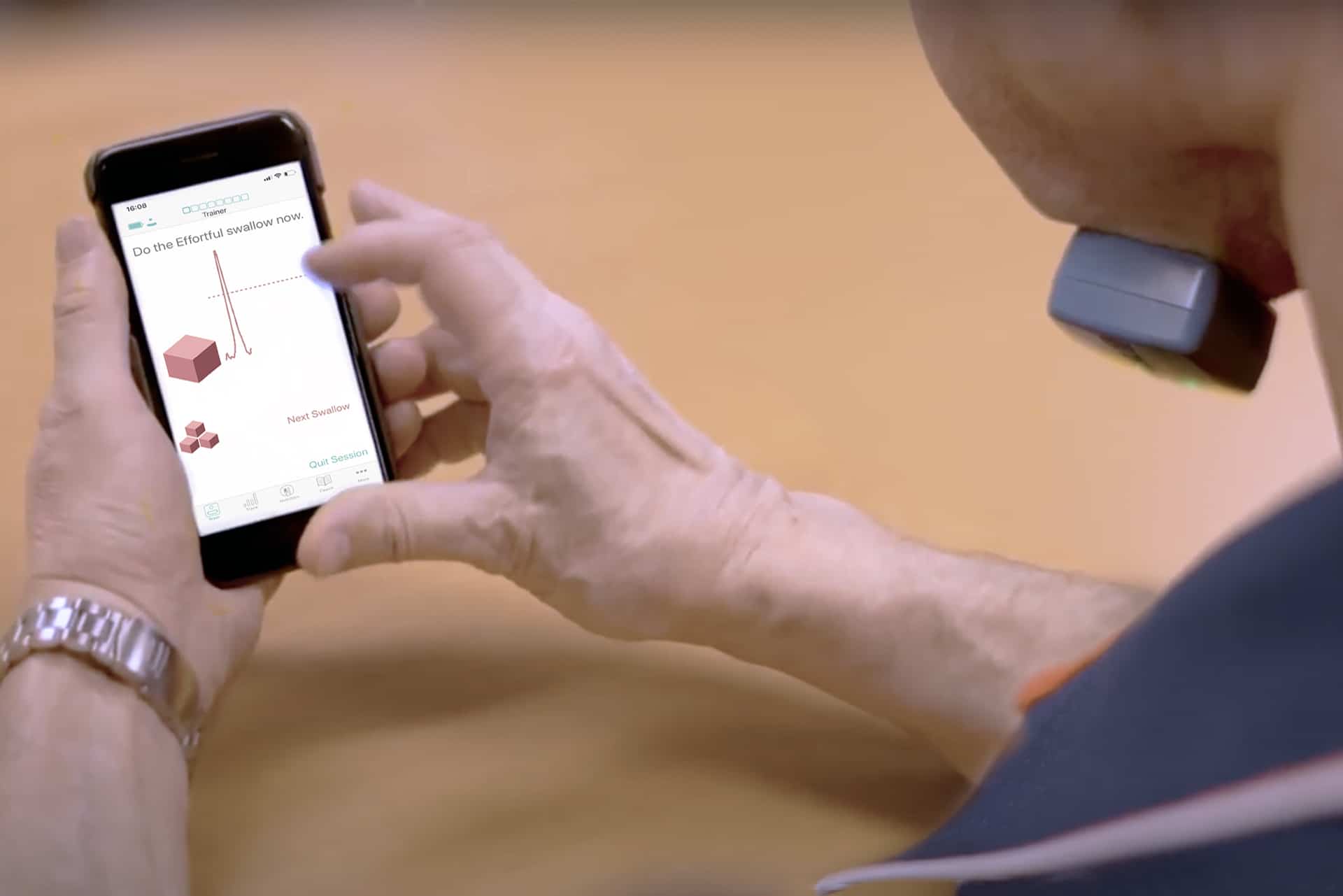
Your patients and clinicians can now level up swallowing exercising with an innovative, portable Mobili-T® device.
With remote digital sEMG biofeedback, clinicians can deliver therapy where they need to, and objectively track adherence to make more precise decisions for better swallowing outcomes.
Higher quality of care for your patients.
Patients are empowered to take control of their own health knowing their data is automatically shared with their healthcare team. Peace of mind replaces after-hour phone calls and avoidable emergency room visits.
Mobili-T is developed and designed by a team of clinicians based on extensive user research. Responsive customer support will provide your team with ongoing support and training to get the best out of the system.
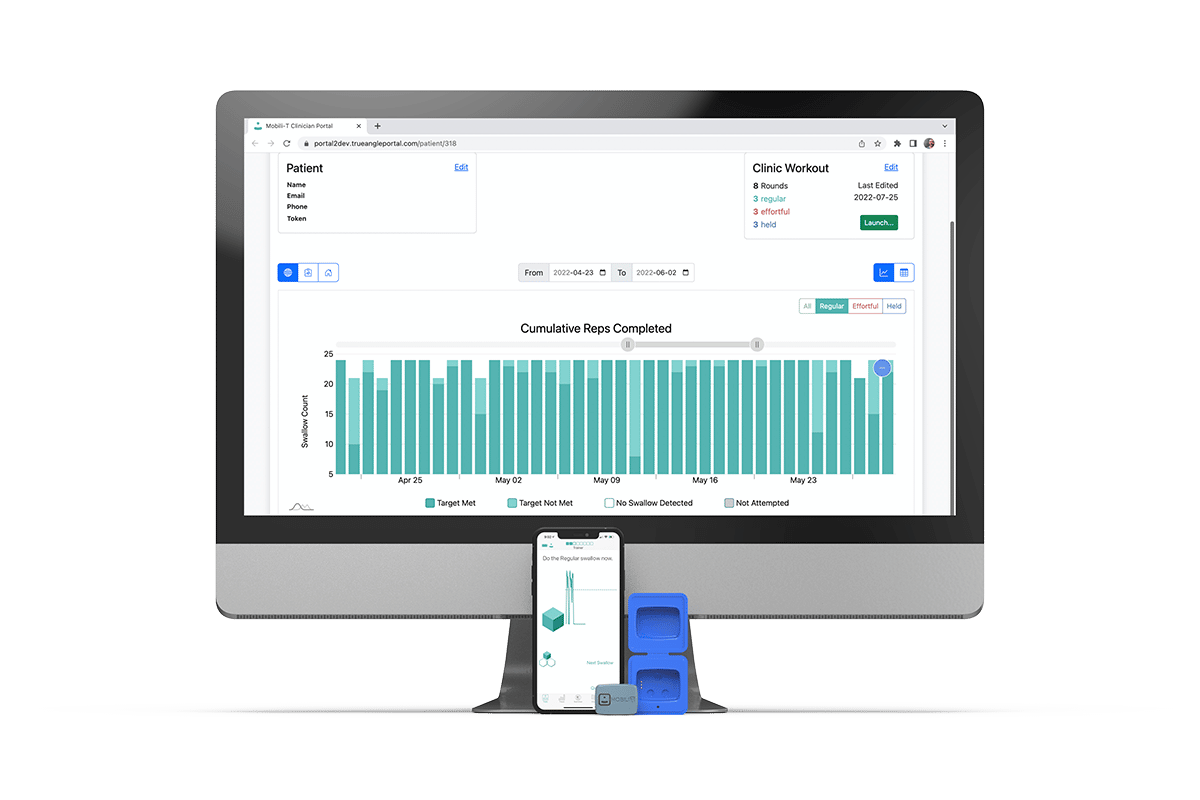

Easy-to-use device and professional packages, with individual clinician portals, to help busy clinicians stay on top of patient progress with the aim of achieving better swallowing outcomes in a more timely fashion.
Not all patients require daily commute or in-hospital care. With Mobili-T’s remote monitoring, clinicians can help patients continue recovery from the comfort of their homes.

Interested in bringing Mobili-T® to your facility?
Looking to see the Mobili-T® system in action or to order an enterprise package for your hospital? Drop us a note here.
References
- Attrill S, White S, Murray J, Hammond S, Doeltgen S. Impact of oropharyngeal dysphagia on healthcare cost and length of stay in hospital: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018 Aug 2;18(1):594. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-3376-3. PMID: 30068326; PMCID: PMC6090960.
- Allen J, Greene M, Sabido I, Stretton M, Miles A. Economic costs of dysphagia among hospitalized patients. Laryngoscope. 2020 Apr;130(4):974-979. doi: 10.1002/lary.28194. Epub 2019 Jul 17. PMID: 31314145.
- Joseph JR, Smith BW, Mummaneni PV, La Marca F, Park P. Postoperative dysphagia correlates with increased morbidity, mortality, and costs in anterior cervical fusion. J Clin Neurosci. 2016 Sep;31:172-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 May 24. PMID: 27234612.
- Cabré M, Serra-Prat M, Force L, Almirall J, Palomera E, Clavé P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a risk factor for readmission for pneumonia in the very elderly persons: observational prospective study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014 Mar;69(3):330-7. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glt099. Epub 2013 Jul 5. PMID: 23833199.
- Callahan CM, Buchanan NN, Stump TE. Healthcare costs associated with percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy among older adults in a defined community. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001 Nov;49(11):1525-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2001.4911248.x. PMID: 11890593.
- Siddique R, Neslusan CA, Crown WH, Crystal-Peters J, Sloan S, Farup C. A national inpatient cost estimate of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG)-associated aspiration pneumonia. Am J Manag Care. 2000 Apr;6(4):490-6. PMID: 10977455.
- Albuquerque LCA, Pernambuco L, da Silva CM, Chateaubriand MM, da Silva HJ. Effects of electromyographic biofeedback as an adjunctive therapy in the treatment of swallowing disorders: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Apr;276(4):927-938. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05336-5. Epub 2019 Feb 15. PMID: 30771061.
- Crary MA, Carnaby Mann GD, Groher ME, Helseth E. Functional benefits of dysphagia therapy using adjunctive sEMG biofeedback. Dysphagia. 2004 Summer;19(3):160-4. doi: 10.1007/s00455-004-0003-8. PMID: 15383945.
- Constantinescu G, Rieger J, Seikaly H, Eurich D. Adherence to Home-Based Swallowing Therapy Using a Mobile System in Head and Neck Cancer Survivors. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2021 Nov 4;30(6):2465-2475. doi: 10.1044/2021_AJSLP-21-00026. Epub 2021 Aug 31. PMID: 34463544.